
With increased interest in animal welfare, groups and institutions are springing up all over the world to rescue and protect animals in distress. This heartwarming story is about a dog rescued from the streets by an Indian animal protection organization. The puppy was badly injured in one ear when it was discovered. His appearance, crying out in agony, breaks the rescuer’s heart. However, the puppy’s behavior changed dramatically after that.
A white dog was discovered on the streets of India one day. The rescuers quickly phoned Animal Aid, an Indian charity that saves and protects animals.

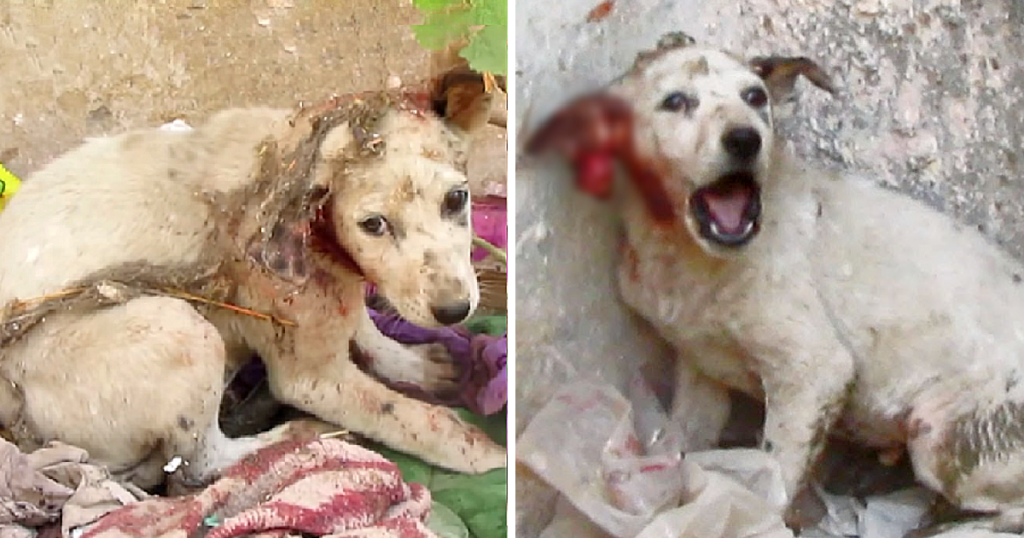
What sort of dog is requesting assistance… Rescue personnel that arrived on the spot were misled. When they noticed the puppy, they took a brief pause.
One ear of the puppy, who was whimpering and sitting on the road’s edge, hung down and was nearly ripped.

A puppy screaming in agony and dangling his bloodied ears. Because it hurt so much, he wailed and tossed his head from side to side. The rescuer approaches the puppy gently and quietly.
The dog, on the other hand, was terrified and in pain. She wept and retreated from Zurizuri and her rescuers.

Close inspection indicates that the hair is sticking to the surrounding dust, grass, and dust.
The rescuer provided food to the dog, but the puppy was in such much pain that he refused any food.
In the face of such a dog, rescue workers never give up. I wish to relieve this child’s pain. She might have other injuries.

He took his time approaching the puppy and wrapped a blanket around his body. The puppy was then wrapped in a blanket and transported to the Animal Aid center.
The puppy was promptly sedated upon arrival at the institution, and veterinarian care commenced.
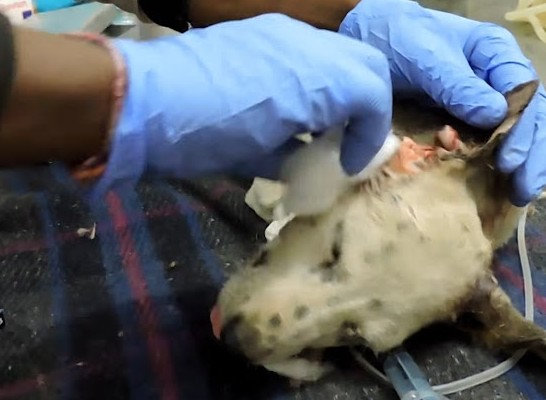
His ears, which are only held together by a sliver of tissue, are medically removed and meticulously sutured. After the dramatic rescue play, the puppy was finally able to rest calmly.
“Banjo” was subsequently given to the dog. In his case, he has only two ears, which is a dog trait. He was also two weeks post-surgery.
Banjo has undergone a significant transformation!
Banjo’s presence two weeks later thrilled the audience. When Banjo was discovered, he was absolutely scared and shaking.
He is now going around and playing with other dogs and people.
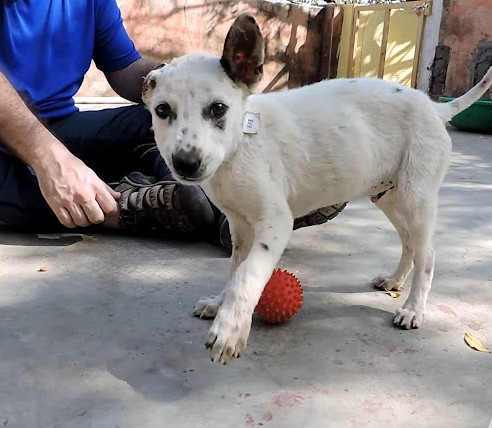

The puppy’s mischievous side is also coming to life. Nobody who discovered him realized he was such a fun and attractive dog at the time.

Some people may ask if it’s okay for a dog to be deaf in one ear. In the case of Banjo, though, he seemed indifferent about losing one of his ears.

I hope Banjo, who has made a moving change, will continue to live happily.
The Journey of Nancy Sinatra: Resilience, Transformation, and Success
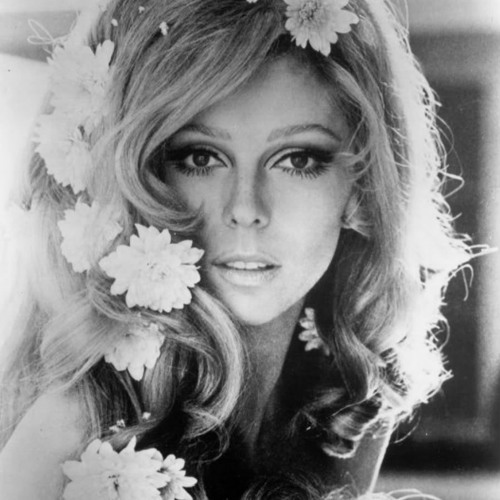

The well-known Frank Sinatra’s daughter, Nancy Sinatra, has never been out of the spotlight. She was exposed to the opulent lifestyle that came along with her father’s fame while growing up in a magnificent New Jersey home. Despite this, the family was concerned about the attention and throngs that collected around their home.
Nancy had to face challenges even though she came from a wealthy background to become a great singer. Due to the poor reception of her early releases, there were even reports that her father’s record label was thinking of removing her. Nancy, though, was unmoved. She embarked on a mission to alter her situation.

Nancy made a triumphant return to the music business by altering her image and undergoing voice training. Her transformation from an unfulfilled artist to a hitmaker is proof of her ability, perseverance, and determination. She is an inspiration to budding artists who are overcoming obstacles in their own lives.
Nancy faced difficulties even though she achieved incredible success in the music industry. After she left college early and discovered that her father’s record business would terminate her, her career seemed uncertain. But everything changed when lyricist Lee Hazlewood offered advice on how to pursue her career.
Singing down an octave, Nancy, with Hazlewood’s assistance, discovered her own voice. Additionally, he helped her update her appearance so that it more closely resembled the trendy “Carnaby Street” image. Nancy’s greatest degree of success was attained with her number-one hits, “Sugar Town,” “How Does That Grab You, Darlin’?” and “These Boots Are Made for Walkin’,” thanks to her renewed concentration. She even made her mark on the big screen, costarring on screen with icons of the motion picture industry like Elvis Presley and Peter Fonda.

Nancy made the decision to step back from the spotlight in the 1970s, even with her many accomplishments, so that she could spend more time with her family. But when she released her third album and posed for Playboy at the age of 54, she stunned everyone. Her work with well-known musicians such as Bono and Morrissey showed that her passion and musical ability were unwavering.
Nancy loved her father so much that she authored two books on his life. In recognition of her commitment to preserving his memory, she was awarded a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame. Her distinct fashion sense—particularly her go-go boots—became strongly linked to her character. Those iconic boots, albeit she no longer owns them, left a lasting impression on her career and image.

Nancy has struggled in her personal life in addition to her musical career. She divorced young singing idol Tommy Sands after a few years of marriage. Nancy made the decision to prioritize her daughters’ schooling over her singing career. During this time, she met Hugh Lambert, who would become her second husband. Their marriage was sadly ended in 1985 when Hugh succumbed to illness.
Nancy Sinatra persevered through personal hardships to pursue a demanding career. Nancy’s Boutique was founded in 2020 as an internet-based shop where fans could purchase CDs, exclusive products, and autographed items. She also hosted the weekly radio show “Nancy for Frank” until 2021, during which she shared personal information about her life and her relationship with her late father.

Nancy has a vivid and strong personality that has inspired many, and her contributions to the music industry are absolutely remarkable. As long as she continues to pursue a wide range of activities, she will undoubtedly be recognized as a representative of her generation. Nancy Sinatra led a life marked by unwavering determination, transformation, and unmatched success.



Leave a Reply