When it comes to cooking up a storm in the kitchen, ground beef is a culinary superhero. From tacos to spaghetti, this versatile ingredient has the power to turn a simple meal into a flavor-packed feast. But there’s a lingering question that divides kitchen warriors: Should you rinse your ground beef before cooking (or after)?
Some kitchen enthusiasts swear by rinsing their ground beef before (and after) cooking, and they have a few compelling reasons. First and foremost, rinsing can help reduce the fat content of the meat. If you’re trying to cut down on calories or simply want a leaner dish, giving your ground beef a quick rinse under hot water might be the trick.
Rinsing can also help eliminate excess grease, preventing your dish from turning into an oily mess. Imagine a perfect plate of spaghetti, where the star of the show isn’t overshadowed by a pool of unwanted fat. Rinsing can be the hero that sаvеs your meal from becoming a greasy catastrophe.
On the flip side, many cooks argue that rinsing ground beef is a culinary sin. One of the primary concerns is flavor loss. When you rinse ground beef, you risk washing away not only the fat but also some of the savory juices that make your dish delicious. After all, who wants a bland and dry burger when you were aiming for a flavor explosion?
Another point against rinsing is that it can be a messy affair. Picture yourself at the sink, trying to juggle a pound of ground beef while hot water splashes around. It’s not the most glamorous part of cooking, and the cleanup might not be worth the potential benefits.
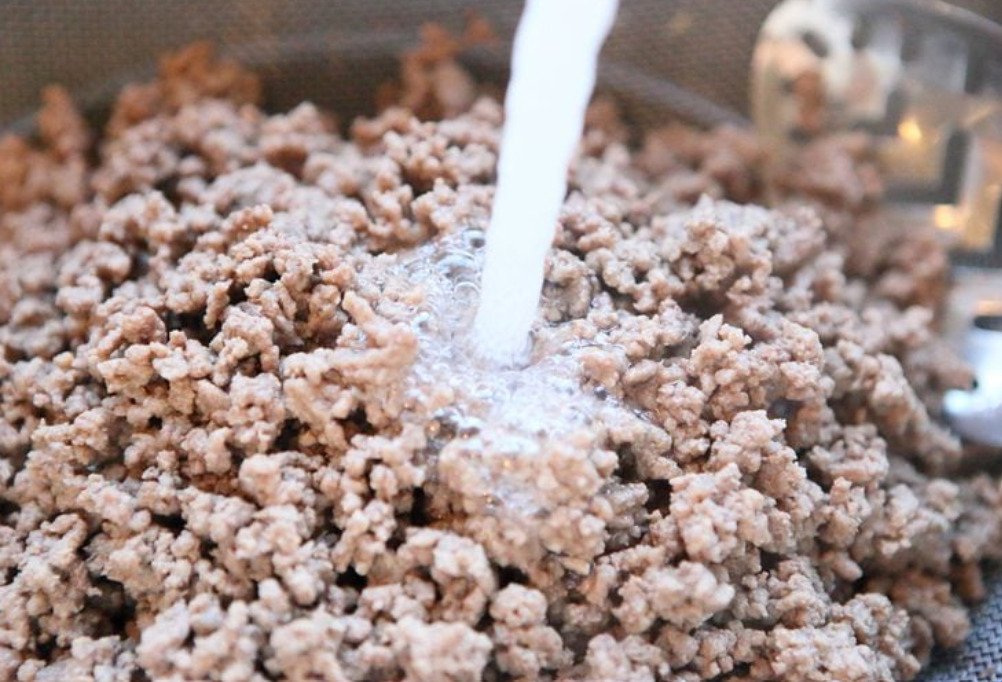

While rinsing fat from ground beef down the sink might seem likе a convenient solution, it can lead to serious plumbing issues. As the fat cools, it solidifies and can clog pipes over time. This creates a recipe for disaster, potentially causing blockages, slow drainage, and even the need for costly plumbing repairs.
Dispose of fat from ground beef by letting it cool and solidify, then scrape it into a sealable container. Toss the container in the trash, preventing plumbing issues caused by pouring fat down the sink. Proper disposal ensures a smooth-running kitchen and avoids potential pipe blockages.
So, should you rinse your ground beef? The answer depends on your culinary goals and personal preferences, but our short answer is no. If you’re a flavor enthusiast who wants every drop of deliciousness, skipping the rinse is the way to go.
Whether you’re Team Rinse or Team No-Rinse, the most important thing is to enjoy the process of creating mouthwatering meals. In the end, the choice is yours.
There’s One Method of Healing Trauma That Prince Harry Uses, and Here’s How to Practice It
Prince Harry recently opened up about his journey with post-traumatic stress disorder following the loss of his mother, Princess Diana. In a candid discussion, he revealed his exploration of a groundbreaking therapy that helped him.
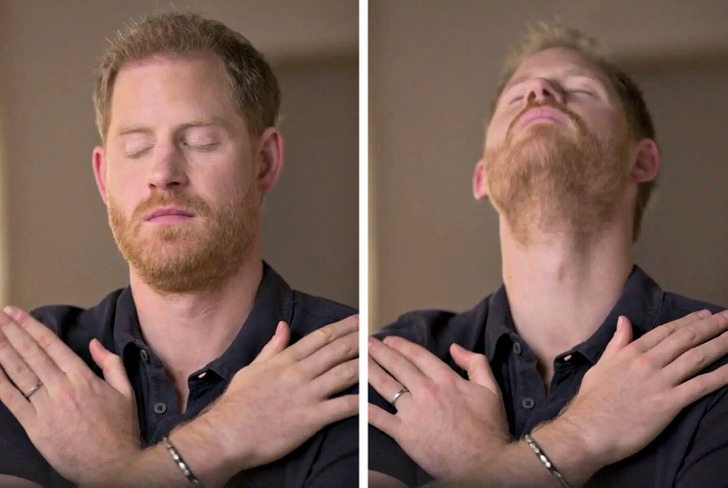

The therapy is called eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) to address the debilitating effects of his anxiety attacks. This revelation offers a glimpse into the royal’s personal struggles and his proactive approach towards mental health care, shedding light on the significance of seeking innovative treatments of traumas.
In a video, Prince Harry can be seen undergoing EMDR therapy, where he taps his shoulders and moves his eyes rapidly. This therapy is relatively new and is used to treat PTSD. Prince Harry shared that he decided to try EMDR to deal with severe anxiety attacks he was experiencing.
Prince Harry mentioned that he was open to trying EMDR because of the therapy and work he had done over the years.
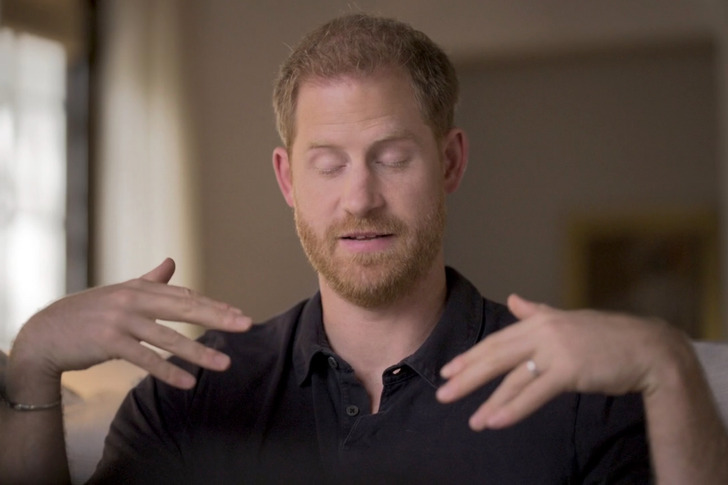

During a therapy session with UK-based psychotherapist Sanja Oakley, Prince Harry demonstrated how EMDR helped him feel better about returning home. He described feeling scared and helpless before, but the therapy helped him cope with those feelings.
Prince Harry’s openness about his experience with EMDR therapy sheds light on alternative treatments for post-traumatic disorder and mental health struggles. It shows that seeking help and trying different therapies can make a difference in managing mental health conditions.

EMDR is a therapy made in 1987 to help with emotional traumas. It’s a structured therapy where you think about a tough memory while moving your eyes back and forth. This helps lessen the strong feelings tied to the memory.
EMDR works on a theory called Adaptive Information Processing (AIP). It says that trauma sticks around because it hasn’t been dealt with properly. So, when something reminds you of the trauma, those memories can come back strongly.
Unlike other therapies that try to lessen your reaction to trauma, EMDR tries to change how your brain stores those tough memories. Sometimes, instead of eye movements, you might listen to alternating tones. Usually, EMDR happens once or twice a week for about six to 12 sessions. But it can vary depending on the person.
Benefits of EMDR therapy
- EMDR is a structured therapy and usually needs fewer sessions than ongoing therapies.
- You don’t have to keep going back to the tough memory for a long time.
- You don’t have to talk a lot about what happened to you.
- There’s no homework to do.
- EMDR doesn’t try to change your thoughts and beliefs.
Disadvantages of EMDR therapy
- While EMDR is known to help with PTSD, it hasn’t been studied as much for other mood or mental health problems.
- If you’re avoiding talking about a tough event, EMDR might not be the best choice. Other types of talk therapy might work better.
- EMDR can sometimes make you feel worse at the start of treatment. The person who created EMDR warns that this could be dangerous for people who have gone through really tough things.
The process of EMDR
EMDR is a structured process with eight phases, each aimed at helping you deal with traumatic memories:
- History taking: Discuss your past with the therapist to identify which memories to focus on.
- Preparation: Learn about EMDR and how the therapist will use bilateral stimulation.
- Assessment: Identify your negative and positive beliefs related to the trauma.
- Desensitization: Use bilateral stimulation while recalling the memory.
- Installation: Focus on positive beliefs while processing the memory.
- Body scan: Talk about how you feel emotionally and physically.
- Closure: Prepare for what may happen between sessions.
- Reevaluation: Assess your progress and decide if more sessions are needed.
As you go through EMDR, you may start feeling less overwhelmed by the trauma. It’s normal for other painful memories to surface, indicating that suppressed memories are being processed.
When grappling with deep emotional traumas, it’s crucial to seek out specialists who can provide the appropriate form of treatment tailored to your needs. Whether it’s EMDR therapy or other therapeutic approaches, finding the right professional can make a significant difference in your healing journey.
Preview photo credit Good Morning America / YouTube


Leave a Reply