Jessica McLane, now 30 years old, reminisces about her time at Hendersonville High School in Nashville, Tennessee, where she claims to have briefly crossed paths with none other than Taylor Swift, the now 32-year-old global pop sensation. McLane’s account sheds light on the dynamics surrounding Swift’s rise to fame within the confines of her high school years.
During McLane’s fleeting time at Hendersonville High in 2006, she found herself in the same academic environment as Swift, who had already begun to make waves in the music industry. Swift, a native of Wyomissing, Pennsylvania, had relocated to Tennessee at the age of 14 to pursue her dreams of becoming a country music star. By the time McLane encountered her, Swift was already well on her way to stardom.
McLane’s recollections offer a glimpse into the complex social dynamics at play within the high school environment. She suggests that Swift’s growing success may have elicited feelings of jealousy and resentment among some of her peers. According to McLane, “a lot of the singer’s fellow students ‘hated’ her because they were ‘jealous’” of her burgeoning music career.
Swift’s journey from small-town Pennsylvania to the epicenter of the country music scene in Nashville undoubtedly set her apart from her peers. As she navigated the halls of Hendersonville High, her aspirations and achievements may have created a sense of unease or insecurity among those who struggled to reconcile her rapidly ascending star status with their own experiences.
McLane’s account challenges the romanticized narrative often associated with Swift’s rise to fame, highlighting the less glamorous aspects of her journey. Despite Swift’s undeniable talent and ambition, her path to success was not without its challenges, including navigating the complexities of high school social dynamics while simultaneously pursuing her music career.
The images accompanying McLane’s story offer a visual representation of Swift’s time at Hendersonville High, capturing her youthful exuberance and determination. From candid snapshots to yearbook portraits, these visuals provide a glimpse into the formative years of a future music icon.
Swift’s tenure at Hendersonville High lasted for two-and-a-half years before she ultimately made the decision to leave and pursue homeschooling as her music career continued to gain momentum. Her departure marked the end of an era for both Swift and her classmates, signaling the beginning of a new chapter in her extraordinary journey.
McLane’s reflections serve as a reminder that even the most iconic figures in popular culture have humble beginnings rooted in everyday experiences. Swift’s time at Hendersonville High may have been marked by moments of triumph and adversity, but it undoubtedly played a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of her career and shaping the person she would ultimately become.
As Swift continues to dominate the music industry and inspire millions of fans around the world, stories like McLane’s offer a valuable glimpse into the early days of her ascent to superstardom. They remind us that behind the glitz and glamour lies a journey fueled by passion, perseverance, and the unwavering belief in the power of one’s dreams.
Céline Dion Shares Raw Video of Stiff-Person Syndrome Crisis in Never-Seen Footage from New Documentary
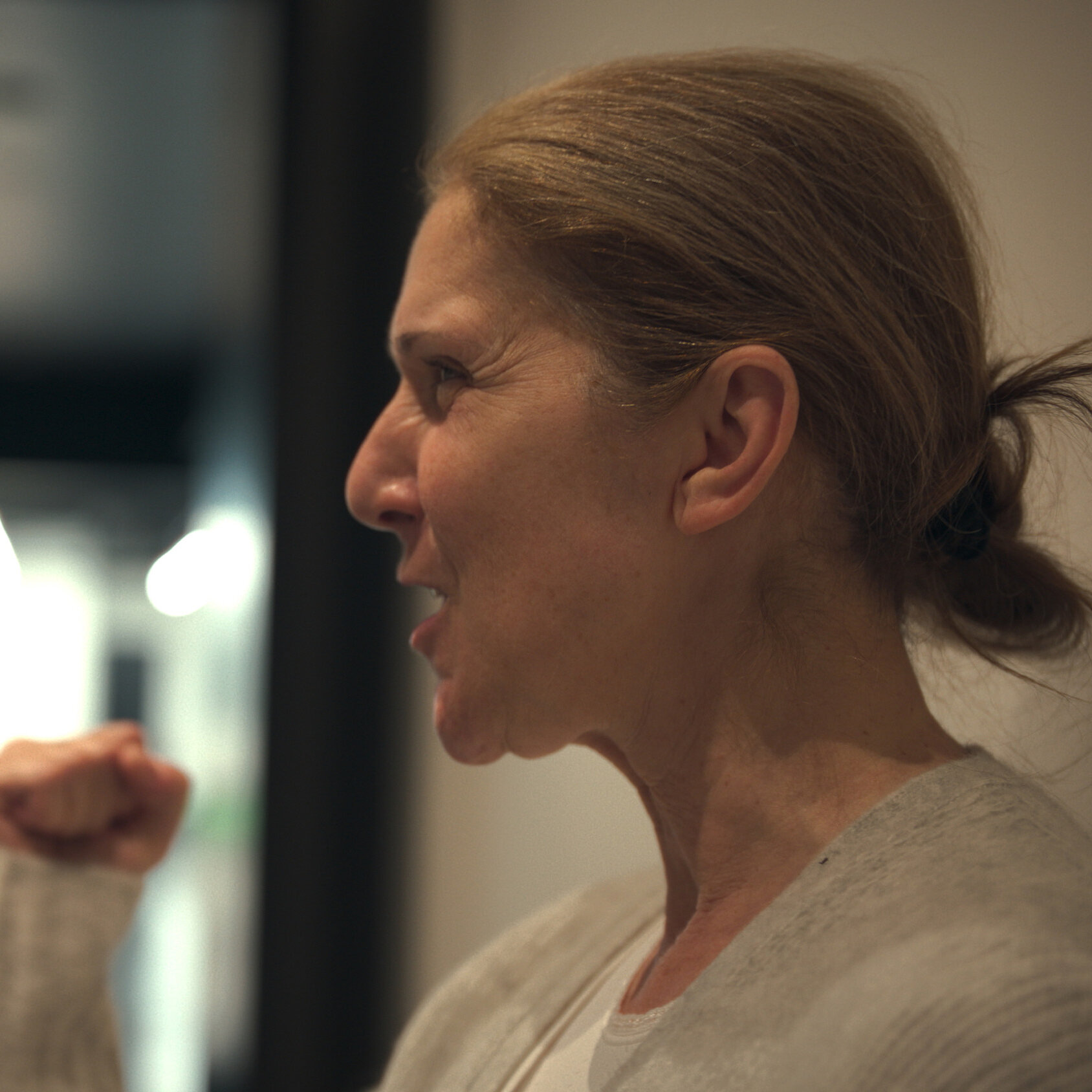

In a devastating moment from “I Am: Céline Dion,” the famous person battles through an unexpected and horrifying SPS episode.

Fans are getting an unheard-of glimpse inside Céline Dion’s tribulations during the last few years of her life.
After being diagnosed with stiff-person syndrome in August 2022, the 56-year-old superstar tentatively but proudly returns to the recording studio in a devastating sequence towards the end of her new documentary, I Am: Céline Dion (available for streaming globally on Prime Video).
Shortly after, as part of her continuous treatment regimen, she makes her way to physical therapy and her foot starts to hurt.
Dion’s body locks up, indicating that she is in severe agony while her care team gives her a diazepam nasal spray during the SPS crisis episode. One of her teammates says, “We’ll do a 9-1-1 if she goes back into a spasm.”
In the movie, Dion subsequently remarks, “Every time something like this happens, it makes you feel so embarrassed.” “I’m not sure how to say it. You know that you dislike losing control of yourself?
The five-time Grammy winner thought back on the horrifying moment that director Irene Taylor’s crew captured on camera during her PEOPLE cover interview.
“Overstimulation—whether it be happiness, sadness, sound, or a surprise—can put me into a crisis—that’s one part of the [SPS] condition,” Dion explains, adding that she “did not see” the crisis episode coming that day. “Before something triggered, I was fine.”
Taylor’s understanding of the condition deepened when she was “two feet away” from Dion during the crisis.
Taylor remarks, “That was really amazing, not just for Céline to go through it, but for me to see as well.” “I continued to film because that is how I work, and I thought we would decide later whether or not to incorporate that into the movie.”

Dion and Taylor had developed a close relationship by the time the movie was in post-production, and according to Taylor, “I knew that putting it in the film was really not a risk because she believed in me at that point.” “I really can only thank her for that because she is an open book, was there, and didn’t hold anything back.”
Dion is attempting to humanize the uncommon illness through the movie and contribute to fund-raising efforts for scientific studies in the pursuit of a solution.
Neuropathy has a very broad spectrum. For this reason, I’m making a lot of effort to raise money so that people can speak with their husbands, friends, or neighbors about it,” Dion explains.
Adds Dr. Amanda Piquet, the doctor who diagnosed Dion and director of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus’s program on autoimmune neurology: “There are many exciting things in store for SPS, and the future looks bright.”



Leave a Reply